Theme: New Therapeutic Mechanisms of Diabetes
diabetes meeting 2019
Welcome to the Diabetes Meeting 2019!
With the amalgamation of peerless speakers of Diabetes 2018 Conference Series is privileged to announce its “30th Diabetes Conference” which will be held during October 21-22, 2019 at Zurich, Switzerland. We cordially welcome all the eminent researchers, students and delegates to take part in this upcoming Diabetes conference to witness invaluable scientific discussions and contribute to future innovations in the field of Diabetes.
According to WHO, about 60 million people with diabetes in the European Region. About 10.3% of men and 9.6% of women aged 25 years and over. Worldwide, high blood glucose kills about 3.4 million people annually amongst 80% of these deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries, and almost half are people aged under 70 years. WHO projects diabetes deaths will double between 2005 and 2030. The overall risk of death among people with diabetes is at least double the risk of their peers without diabetes. Reflecting this imperative, Conference Series is all set to host Diabetes conference in Berlin, Germany this year which will provide the future leadership in this key area for global health.
Diabetes Meeting 2019 will focus on the latest and exciting innovations in all areas of Diabetes research which offers a unique opportunity for investigators across the globe to meet, network, and perceive new scientific innovations. This year’s annual congress highlights the theme, “New Therapeutic Mechanisms of Diabetes” which reflects the innovative progress in Diabetes research. The two days conference includes workshops, symposiums, special keynote sessions conducted by eminent and renowned speakers who excel in the field of Diabetes which include: Advanced Technologies for Treatment of Diabetes, Emerging Focus in Diabetes Research, Diabetes Research in Clinical Practice, Computational Biology of Diabetes, Cell Therapy for Diabetes and its Complications, Genetics of Diabetes, Diabetes Management, Transplantation for Diabetes, Endocrinology Disorders and Treatment.
Why Zurich?
Zurich is a leading global city and among the world’s largest financial centers despite having a relatively low population. The city is home to a large number of financial institutions and banking giants. Most of Switzerland’s research and development centers are concentrated in Zurich and the low tax rates attract overseas companies to set up their headquarters there. Many museums and art galleries can be found in the city, including the Swiss National Museum and the Kunsthaus. According to several surveys from 2006 to 2008, Zurich was named the city with the best quality of life in the world as well as the wealthiest city in Europe.
The Economist Intelligence Unit’s Global Liveability Ranking sees Zurich ranks among the top ten most liveable cities in the world. Zurich has, depending on the definition used, an oceanic climate (Koppen Cfb), with four distinct seasons. Decisive for the climate of Zurich are both the winds from westerly directions, which often result in precipitation and, on the other hand, the Bise (east or north-east wind), which is usually associated with high-pressure situations, but cooler weather phases with temperatures lower than the average. The Foehn wind, which plays an important role in the northern alpine valleys also, has some impact on Zurich.
The city of Zurich is among the world leaders in protecting the climate by following a manifold approach. Public transport is extremely popular in Zurich, and its inhabitants use public transport in large numbers. Zurich city highlights are The nation’s biggest lakes—Geneva, Constance (Bodensee), and Maggiore— straddle the French, German-Austrian, and Italian outskirts, individually. The Rhine, safe from Basel toward the North Sea, is the key inland waterway, National Museum Zurich, Platzspitz – a Historic Park at the Heart of Zurich, Hans Waldmann – a Military Leader and Mayor of Zurich in the Late Middle Ages. About 70% of the visitors to the city use the tram or bus, and about half of the journeys within the municipality take place on public transport. Within Zurich and throughout the canton of Zurich, the ZVV network of public transport has traffic density ratings among the highest worldwide.
We look forward to meeting you at Zurich, Switzerland
Track 01: Complications associated with Diabetes
The term diabetes mellitus describes several diseases of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism that are characterized by hyperglycaemia. It is associated with a relative or absolute impairment in insulin secretion, along with varying degrees of peripheral resistance to the action of insulin. They are derived after doing many clinical trials on animal models. Every few years, the diabetes community revaluates the current recommendations for the classification, diagnosis, and screening of diabetes, reflecting new information from research and clinical practice which in turns help in understanding current prevention and treatment options and cost effectiveness in treatment and prevention of Diabetes. People with type1 and type2 diabetes have an increased risk of developing a number of serious health problems. Consistently high blood glucose levels can lead to serious diseases affecting the Macro vascular and micro vascular complications. In addition, people with diabetes also have a higher risk of developing infections. In almost all high-income countries, diabetes is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, blindness, kidney failure, and lower limb amputation. Maintaining blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol at or close to normal can help delay or prevent diabetes complications. Hypoglycaemia and Hyperglycaemia are the other two factors are the two major complications of diabetes where hyperglycaemia is an acute complication sharing many symptoms and hypoglycaemia is an acute complication of several diabetes treatments. Glycosylated haemoglobin is a form of haemoglobin that is measured primarily to identify the average plasma glucose concentration over prolonged periods of time.
Track 02: Genetics of Diabetes
Diabetes constitutes a major public health problem. Although substantial progress has been made in defining the genetics of metabolic syndrome risk for specific subtypes of diabetes (e.g., maturity-onset diabetes of the young), the majority of genetic risk of diabetes (for type 1 and type 2) remain unresolved. This review focuses on the current knowledge of the genetic basis of diabetes and its complications, specifically diabetic nephropathy (DN), recent advances in genetics of diabetes, diabetes in ethnic groups, genetic lifestyle interactions and understanding the genetics of Diabetes. Ultimately, identification of genes that contribute to risk (or protection) of diabetes and its complications will allow identification of patients who have diabetes and are at risk and targeted treatment/interventional strategies. Diabetic amyotrophic is a disabling illness that is distinct from other forms of diabetic neuropathy.

Track 03: Advanced Technologies for the Treatment of Diabetes
The concept of 'new technologies' for type 1 diabetes and new discovery and advanced type 2 diabetes treatment has expanded in recent years at a rate that some might consider comparable to 'Moore’s Law', and the sheer number of new technologies entering into the type 1 diabetes marketplace is also growing at a remarkable rate. From the patient’s perspective, this is not only exciting but can lead to a sense of optimism. Technologies that today are growing commonplace (e.g. insulin pumps, rapid HbA1c monitoring, etc come under new therapeutic mechanisms of diabetes. Indeed, it could be argued that the major advances in type 1 diabetes care made within the last quarter of a century have come from technology rather than biology. At the same time, not all new technologies succeed (e.g. the Glucowatch), regardless of their purported promise. Both type 1 diabetes patients and their healthcare providers will soon see a series of further advanced medical technologies used in hospital and new technologies and novel therapies in diabetes treatment whosbasis is tied to the notion of improving the lives of those with the disease.
Track 04: Diabetes Management
The main goal of diabetes management is, as far as possible, to restore carbohydrate metabolism to a normal state. To achieve this goal, individuals with an absolute deficiency of insulin require insulin replacement therapy, which is given through injections or an insulin pump. Insulin resistance, in contrast, can be corrected by dietary modifications and exercise. Other goals of diabetes management are to prevent or treat the many complications that can result from the disease itself and from its treatment. Healthy eating is a cornerstone of healthy living — with or without diabetes. But if you have diabetes, you need to know Impact of Food and Nutrition, impact of physical activity and yoga therapy in Diabetes Management. Diabetic foot complications result in huge costs for both society and the individual patients. Few reports on the health-economic consequences of diabetic foot infections have been published. Standards of medical care in Diabetes increased when compared to previous year.
Track 05: Emerging Focus in Diabetes Research
Diabetes is a common chronic disease that imposes considerable demands on the individual healthcare system. People with diabetes have a higher rate of cardiovascular disease than those without diabetes and are at increased risk for kidney failure, lower limb amputation and blindness. Obesity is a significant risk factor for diabetes and the prevalence of obesity in children and adults has dramatically increased in the past four decades. Diabetic dyslipidemia is one of the major risk factors for cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. The characteristic features of diabetic dyslipidemia are a high plasma triglyceride concentration, low HDL cholesterol concentration and increased concentration of small dense LDL-cholesterol particles. In order to investigate the bioinformatics tools and methodologies used to in diabetes research, at first, this was difficult to do because it did not have a preconceived idea about how the research would be organized and how bioinformatics tools would be described or identified in the research. To get started, we ran several cursory searches using basic search terms such as bioinformatics and diabetes (research) through several databases to see what types of articles were returned. Diabesity can be defined as a metabolic dysfunction that ranges from mild blood sugar imbalance to full-fledged type 2 diabetes. A bolus dose is insulin that is specifically taken at meal times to keep blood glucose levels under control following a meal.
Track 06: Transplantation of Diabetes
Getting a new heart, liver, kidney, lung, or other organ can save your life. Sometimes, it can also lead to type 2 diabetes. Many people can stop taking steroids after 6 months or so. This may solve the problem. If scientists can develop safe immunosuppressant’s that always work, then many people with type 1 diabetes may choose to have pancreas transplants. Until then, many doctors think islet transplants are a better option even after performing clinical trials on islet transplants. Islets are clusters of cells in the pancreas that make insulin. In people with type 1 diabetes, islet cells are destroyed. Only 1-2% of the pancreas is made up of islet cells. In pancreatic islet transplantation, cells are taken from a donor pancreas and transferred into another person. Once implanted, the new islets begin to make and release insulin. Researchers hope that islet transplantation will help people with type 1 diabetes live without daily injections of insulin. A transplant of the pancreas is usually reserved for those with serious complications. Pancreas transplants are most often done when a patient also receives a new kidney. The pancreas transplant adds little further risk in this situation and offers big benefits. However, transplant surgery is risky. Each person needs to carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks. Xenotransplantation for the treatment of type 1 diabetes is the transplantation of living cells, tissues or organs from one species to another. Such cells, tissues or organs are called xenografts or xenotransplants. A bolus dose is insulin that is specifically taken at meal times to keep blood glucose levels under control following a meal. Bolus insulin needs to act quickly and so short acting insulin or rapid acting insulin will be used where as Conventional insulin therapy is a therapeutic regimen for treatment of diabetes mellitus which contrasts with the newer intensive insulin therapy.
Track 07: Diabetes Research in Clinical Practice
Novel therapeutic targets available for diabetes includes Incretin based therapies, oral therapeutic agents like secretagogues, beta cell regeneration & proliferation and stem cell therapies. Embryonic stem cell and fetal precursor cell transplantation therapies are the major stem cell therapies available for Diabetes. Apart from the above, various computational approaches in Diabetes management control have been introduced recently which are playing an important role in identification of genes causing diabetes helping in Early Detection of Diabetes. These processes are also useful in studying the chemical etiologies of Diabetes uncovering various treatment prospects and model construction processes for survival prediction.
Track 08: Computational Biology of Diabetes
Computational meta-analysis can link environmental chemicals to genes and proteins involved in human diseases, thereby elucidating possible aetiologies. The recent rapid development of a variety of analytical platforms based on mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance have enabled identification of complex metabolic Syndrome phenotypes. Continued development of bioinformatics and analytical strategies has facilitated the discovery of causal links in understanding the pathophysiology of diabetes and its complications.
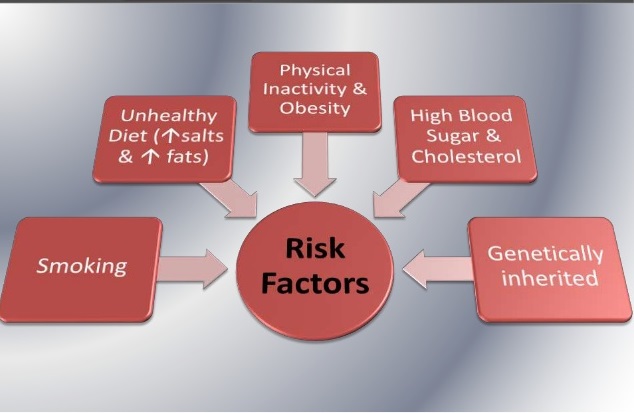
Track 09: Risk Factors and Related Diseases of Diabetes
Diabetes is always accompanied by a number of serious health issues. Consistent increase in blood glucose levels can lead to serious diseases affecting the vital organs of body like heart and blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, nerves and teeth. In almost all high-income countries, diabetes is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease like diabetic cardiomyopathy being one of the major risk factor, blindness, kidney failure, and lower limb amputation. Diabetic Retinopathy causes progressive damage to the retina in the patients with diabetes adding as the most vulnerable risk for the patient. Maintaining blood glucose levels, blood pressure, diabetic gastro paresis which has been reported to have the main cause as Diabetes Mellitus and cholesterol at or close to normal can help delay or prevent diabetes complications.
Track 10: Endocrinology: Disorders and Treatment
Endocrinology is the study of hormones and the treatment of hormone based diseases. The endocrine glands produce chemicals called hormones. These hormones are released into the blood stream and exert their action by stimulating other organs in the body. However, Clinical trials on endocrinology look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease. The major endocrine glands are the thyroid, pancreas, parathyroid, adrenal, gonad and pituitary. The hormones from these glands regulate growth, metabolism, blood pressure, reproduction as well as many other necessary functions. Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Endocrine Disorders, written by a distinguished panel of clinical experts and research scientists, focuses on the early signs and symptoms of common endocrine diseases, surveys the clinical testing needed for a diagnosis, and concisely presents the best current recommendations for therapy. Paediatric endocrinology is a medical subspecialty that studies and treats conditions affecting physical growth and sexual development in children, as well as diabetes and other disorders of the endocrine (hormone) glands.
We are overwhelmed to announce 30th International Diabetes Congress on Prevention of Diabetes and Complications” which is going to be held during October 21-22, 2019 at Zurich, Switzerland. The Conference will be organized around the theme “New Therapeutic Mechanisms of Diabetes”.
This conference highlights the latest and exciting innovations in Diabetes & its Treatment. Diabetes 2019 Conference invites all renowned scientists, endocrinologists, surgeons, dietitians, radiation therapists, general physicians, primary health care specialists, talented young scientists, pharmaceutical industrial delegates and student communities across the globe to attend International Diabetes congress.
Importance & Scope:
Millions of people are suffering and also trying all kinds of diets, pills, and treatments to clear their mental fog, to boost energy and lose weight. Unfortunately, they will all fail unless they learn how to heal the underlying Diabetes issues.
Number of people suffering from Diabetes disorders continues to rise each year. As reported by the World Health Organization (WHO), on an average 1 out of every 13 people are diagnosed globally with Diabetes each year and also projects that diabetes will be the 7th leading cause of death in 2030. Around 60% of the populations effected with Diabetes diseases are uncaring of the situation.
Diabetes Meeting 2019 will feature the latest developments in research, diagnosis and prevention of diabetes, new insulin analogues, new technologies and devices for diabetic prevention, obesity and many more. Not only will this innovative conference enhance your practical and theoretical knowledge but also provides you with the unique opportunity to network with a wide range of professionals in the field of diabetes.
Global Diabetes Prevalence:
The world prevalence of diabetes among adults is 6.4%, affecting 285 million adults in 2010. It will increase to 7.7%, and 439 million adults by 2030. Between 2010 and 2030, there will be a 69% increase in numbers of adults with diabetes in developing countries and a 20% increase in developed countries.
Today’s Market Study of Diabetes in USA | Europe | Middle East | Asia Pacific
Europe: The number of people living with diabetes in Europe is expected to increase from 51 million in 2014 to 67.9 million by 2035, according to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF). Across Europe, around 1 in 11 adults is affected and the number is set to rise as the population ages.
USA: Diabetes Mellitus has been growing at an exponential rate and World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that diabetic population is likely to reach 356 million in 2030. The United States is expected to increase to 102 per cent in the diabetic epidemic in 2030 when compared to 2000
Middle East: The rate of diabetes in Arabian Peninsula is over twice the global average rate and much higher than some other areas of the Middle East and North Africa (MENA).
Asia Pacific: The Asia-Pacific Diabetes Care Devices Market has been estimated at USD 2.521 Billion in 2015 and is projected to reach USD 3.538 billion by 2020, at a CAGR of 7.41% during the forecast period from 2015 to 2020.
Studies show that men have higher rates of diabetes prevalence than women. Women with diabetes are more likely than men with the disease to have poor blood glucose control, be obese, and have high blood pressure and unhealthy cholesterol levels.
Why to attend???
Medical doctors, health care providers consider the prevention of Diabetes diseases as an essential tool to improve the general health status of the population. The proportions of people suffering from the disease are expected to increase in future according to a recent statistical survey. Realizing this imperative, Conference Series is set to organize 30th International Diabetes Congress for the upcoming year with a view to enhance research and promote awareness.
Societies Associated with Diabetes Research
German Diabetes Association
FAND - Italian Association of Diabetics
Italian Association for the Defence of the Interests of Diabetics
Association of Diabetes
Association National Italian Diabetic Athletes
Italian Society of Diabetology
International Diabetes Federation- Italy
Primary Care Diabetes Society
Australian Diabetes Society
Emirates Diabetes Society
Society for Biomedical Diabetes Research
Immunology of Diabetes Society
American Association of Diabetes Educators
American Diabetes Association
The Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes
International Association of the Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups
Diabetes Association of Nigeria
Association of Children's Diabetes Clinicians
Canadian Diabetes Association
For more details, please visit: https://diabetesmeeting.conferenceseries.com/
DISCLAIMER
The information developed in this report is intended only for the purpose of understanding the scope of hosting related international meetings at the respective locations. This information does not constitute managerial, legal or accounting advice, nor should it be considered as a corporate policy guide, laboratory manual or an endorsement of any product, as much of the information is speculative in nature. Conference Organizers take no responsibility for any loss or damage that might result from reliance on the reported information or from its use.
Conference Highlights
- Complications associated with Diabetes
- Genetics of Diabetes
- Advanced Technologies for the Treatment of Diabetes
- Diabetes Management
- Emerging Focus in Diabetes Research
- Transplantation of Diabetes
- Diabetes Research in Clinical Practice
- Computational Biology of Diabetes
- Risk Factors and Related Diseases of Diabetes
- Endocrinology: Disorders and Treatment
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | October 21-22, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Pancreatic Disorders and Therapy
- Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism
- Journal of Steroids and Hormonal Science
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by