About Conference
37th International Congress on Prevention of Diabetes and Complications is a specialized event that brings together leading experts, researchers, healthcare professionals, and stakeholders to discuss the latest advancements, research findings, and clinical practices related to diabetes care and management. These conferences cover a broad range of topics including diabetes pathophysiology, innovative treatments, technology integration such as artificial intelligence in diabetes care, prevention strategies, complications management, and public health approaches to combat the rising global diabetes epidemic.
Diabetes Meeting 2026 include keynote presentations, oral and poster sessions where researchers present original studies, panel discussions, and workshops aimed at fostering collaboration and knowledge exchange among participants. Abstract submissions are carefully peer-reviewed to ensure the presentation of cutting-edge and original work that pushes forward diabetes research and clinical practice. Key goals of this conference is to advance the understanding of disease mechanisms, promote effective prevention and treatment strategies, and improve global diabetes care especially in low- and middle-income countries where disease burden and treatment gaps remain high. These meetings also aim to support policy development, encourage innovative research, and disseminate global guidelines such as those promoted by the World Health Organization and other diabetes associations.
Target Audience:
-
Diabetologists
-
Endocrinologists
-
General practitioners
-
Nurses
-
Students
-
Diabetes educators
-
Pharmacists and dietitians
-
Researchers and clinical scientists
-
Healthcare professionals
-
Policymakers and stakeholders
-
Diabetes patients
Highlights of Diabetes Meeting 2026:
-
Meet the diabetes experts, endocrinologists and diabetologists and dietitians from 45+ countries
-
Meet your peers and evaluate your research in front of experts
-
World-class platform to Exhibit your products and services
-
More than 35 presentations from Industry and Academic leaders
-
Get CPD/CME credits
-
One- to-one interaction and Back to Back Interactions etc.
-
Well organized Scientific Program with 5+ hours of Networking sessions
-
Interactive panel discussions and Q & A sessions
-
Best Poster Awards, Young Research Forums
-
Young Researchers Opportunity
Sessions/Tracks
Diabetes complications arise from prolonged high blood sugar levels, damaging various body systems. Common complications include cardiovascular diseases, neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, and poor wound healing, which can lead to infections and amputations. These complications significantly impact quality of life and increase
healthcare burdens. Early diagnosis, glycemic control, and lifestyle interventions are critical to prevent or delay complications. Regular screenings and patient education play a vital role in managing risks. Research continues to focus on understanding underlying mechanisms and developing targeted therapies to minimize long-term damage caused by
uncontrolled diabetes.
Diabetes treatment aims to manage blood glucose levels and prevent complications. Standard treatments include insulin therapy, oral hypoglycemic agents, lifestyle modifications, and patient education. Newer drugs like GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors offer additional benefits, such as weight loss and cardiovascular protection. Treatment is individualized based on
diabetes type, patient age, comorbidities, and lifestyle.
Continuous glucose monitoring and insulin pumps enhance self-management. Advances in telemedicine and digital health tools support patient adherence. Ongoing research explores immunotherapies, beta-cell regeneration, and potential cures, offering hope for more effective and long-term treatment solutions.
Genetic diabetes includes monogenic forms such as Maturity Onset
Diabetes of the Young (MODY) and neonatal diabetes, caused by mutations in a single gene affecting insulin production. Unlike type 1 or type 2 diabetes, these forms are often misdiagnosed due to overlapping symptoms. Genetic testing plays a crucial role in accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies, which may include oral medications instead of
insulin. Understanding genetic mechanisms enhances precision medicine approaches and improves patient outcomes. Ongoing research in genomics is uncovering new gene variants, aiding in early detection, family screening, and tailored interventions for at-risk individuals.
Effective
diabetes management involves a holistic approach combining medication, diet, physical activity, and regular monitoring. Patient education is critical to ensure adherence and self-care. Monitoring
blood sugar levels helps adjust treatment plans and avoid hypo- or hyperglycemia. Multidisciplinary care teams, including endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators, support personalized management strategies. Lifestyle interventions, such as weight control and stress reduction, play a central role. Digital tools like apps and CGM systems enhance real-time decision-making. Long-term success in diabetes management reduces complications and improves quality of life. Empowering patients with knowledge and tools is essential for sustainable control.
Thyroid disorders affect metabolic regulation and are often associated with diabetes. Conditions like hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and autoimmune thyroid diseases such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease can alter glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
Diabetics, especially those with type 1 diabetes, are at higher risk of thyroid dysfunction. Symptoms may include fatigue, weight changes, irregular heartbeat, or mood swings. Early detection through thyroid function tests and effective hormone replacement or suppression therapy can prevent complications. Managing thyroid disorders in
diabetics requires a coordinated approach involving endocrinologists and regular monitoring to ensure optimal hormonal and glycemic balance.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is an autoimmune condition where the immune system destroys pancreatic beta cells, resulting in absolute insulin deficiency. It typically develops in childhood or adolescence but can occur at any age. Symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. Management involves lifelong insulin therapy,
blood glucose monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments. Advances in insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitors, and closed-loop systems have improved glycemic control. Research is exploring immunotherapies and beta cell regeneration. With proper care, individuals with
type 1 diabetes can lead healthy, active lives despite the chronic nature of the disease.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by
insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. It is the most common form of diabetes, often associated with obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition. Symptoms develop gradually and may include fatigue, blurred vision, and increased thirst. Management includes diet, exercise, oral hypoglycemics, and sometimes insulin. Lifestyle interventions are critical for prevention and control. Innovations like GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, and digital health tools have expanded treatment options. Early diagnosis and continuous monitoring are key to preventing complications. With effective care,
type 2 diabetes is manageable and sometimes reversible.
Recent innovations in
diabetes education emphasize personalized learning, digital tools, and patient empowerment. Mobile apps, virtual coaching, and gamification offer engaging methods to improve self-management skills. Interactive platforms now deliver culturally tailored content and real-time feedback, enhancing comprehension and retention. Peer-support networks and tele-education allow ongoing access to guidance, especially in underserved areas. These innovations aim to increase health literacy, promote behavioral change, and reduce complications. Educators now integrate emotional support and motivational interviewing to address psychological barriers. With evolving technology,
diabetes education is becoming more accessible, adaptive, and effective, leading to better outcomes and patient-centered care.
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in
glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, linking it to the development and management of diabetes. Imbalances in gut bacteria—known as dysbiosis—can trigger inflammation, alter hormone regulation, and impair glucose tolerance. Research shows that specific bacterial strains may either increase or reduce
diabetes risk. Diet, probiotics, and prebiotics are being explored to modulate the microbiome and improve metabolic health. Understanding microbiome-host interactions offers promising strategies for early intervention, prevention, and personalized treatment of both type 1 and
type 2 diabetes. Microbiome-focused therapies may revolutionize future diabetes management approaches.
Effective
diabetic clinical care and prevention focus on early diagnosis, patient education, lifestyle modification, and regular monitoring. Preventive strategies target at-risk individuals through screening, nutrition counseling, weight management, and physical activity. Clinicians utilize tools like HbA1c tests, CGM, and risk calculators to tailor care plans. Evidence-based guidelines support medication adherence, comorbidity management, and behavior change. Collaborative care teams—including
endocrinologists, dietitians, and educators—ensure comprehensive support. Preventive care reduces the onset of complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and
cardiovascular disease. With timely intervention and holistic management, the burden of diabetes can be significantly minimized.
Diabetes and mental health are deeply interconnected, with emotional stress, anxiety, and depression commonly affecting those living with the disease. The daily demands of
blood sugar monitoring, dietary restrictions, and medication adherence can lead to burnout and diabetes distress. Mental health challenges may worsen glycemic control and reduce self-care motivation. Integrating psychological support into diabetes management is vital. Cognitive-behavioral therapy, peer counseling, and mindfulness techniques help patients cope with emotional burdens. Addressing mental health not only improves quality of life but also enhances metabolic outcomes. A holistic care approach is essential for sustainable
diabetes management.
Multiple risk factors contribute to
diabetes, including genetics, obesity, physical inactivity, poor diet, and age. Family history and ethnicity also increase susceptibility.
Type 2 diabetes is often linked with metabolic syndrome, characterized by high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol, and abdominal obesity. Related diseases include cardiovascular disease, stroke, kidney disease, and vision impairment. Persistent hyperglycemia can damage blood vessels and organs, leading to complications. Preventive efforts target modifiable risks through lifestyle changes and regular screenings. Understanding these risk factors and comorbid conditions allows healthcare providers to design proactive, individualized treatment strategies and reduce the long-term burden of
diabetes.
Endocrinology encompasses the study of hormone-producing glands and disorders like diabetes, thyroid disease, adrenal insufficiency, and pituitary dysfunction.
Diabetes mellitus is a central focus due to its widespread impact on metabolism. Treatment often involves hormone replacement, medications to regulate blood sugar or hormone levels, and lifestyle modification. Advances in endocrinology include precision medicine, gene therapy, and bioengineered hormones.
Endocrinologists work closely with other specialists to manage complex cases and coexisting conditions. Patient education, diagnostic imaging, and lab testing play vital roles in care. The field continues to evolve with emerging therapies that improve disease control and quality of life.
Obesity significantly increases the risk of type 2 diabetes by disrupting metabolic processes such as insulin signaling and lipid metabolism. Excess fat, particularly visceral fat, promotes chronic inflammation and insulin resistance. Metabolic syndrome—a cluster of conditions including obesity, high blood pressure, and dyslipidemia—further heightens
diabetes risk. Weight loss through diet, physical activity, and behavioral therapy improves insulin sensitivity and glycemic control. Pharmacological and surgical interventions like GLP-1 agonists and bariatric surgery offer additional options. Understanding the link between obesity and metabolic dysfunction is essential in preventing and managing diabetes. Targeting metabolic health is a core strategy in
diabetes care.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) technologies provide real-time tracking of glucose levels, transforming diabetes management. These wearable sensors measure interstitial glucose every few minutes and offer trends, alerts, and predictive insights. CGM improves glycemic control, reduces hypoglycemic events, and empowers patients to make informed decisions about diet, activity, and medication. Integrated with insulin pumps or mobile apps, CGM supports personalized, data-driven care. Modern CGMs are minimally invasive, accurate, and user-friendly. They are particularly beneficial for
type 1 diabetes and insulin-dependent type 2 patients. As technology advances, CGM is becoming a cornerstone of modern
diabetes therapy.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing
diabetes management by enhancing prediction, diagnosis, and personalized treatment. AI-powered apps analyze glucose data, recommend insulin doses, and track lifestyle factors. Machine learning algorithms can identify risk patterns and predict complications like
diabetic retinopathy or hypoglycemia. AI also supports clinical decision-making by integrating patient data and evidence-based guidelines. Virtual assistants and chatbots improve patient engagement and education. In research, AI accelerates drug discovery and genomics analysis. While challenges like data privacy and algorithm bias remain, AI has enormous potential to optimize outcomes and streamline care for individuals living with
diabetes.
Diabetic nephropathy is a kidney complication caused by long-term uncontrolled diabetes, leading to progressive renal damage. It is characterized by proteinuria, reduced glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and eventual kidney failure if untreated. High
blood sugar levels damage the kidney’s filtering units, and hypertension accelerates progression. Early detection through urine albumin tests and regular monitoring is crucial. Management includes strict glycemic and blood pressure control, use of ACE inhibitors or ARBs, and lifestyle changes. Advanced stages may require dialysis or kidney transplantation. Preventive care and early intervention significantly reduce the burden of
diabetic nephropathy on individuals and healthcare systems.
Diet plays a central role in diabetes control, with certain dietary patterns improving blood glucose, weight, and lipid profiles. Low glycemic index foods, fiber-rich diets, and Mediterranean-style eating have shown positive outcomes. Carbohydrate counting, portion control, and consistent meal timing help regulate
blood sugar. Emerging research supports plant-based diets and intermittent fasting for improved insulin sensitivity. Individualized meal plans based on cultural preferences and metabolic needs are essential. Registered dietitians provide education and support to enhance adherence. A balanced, nutrient-dense diet, combined with lifestyle changes, remains a foundational pillar in effective
diabetes management.
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Persistent hyperglycemia contributes to endothelial dysfunction, atherosclerosis, and inflammation. Other coexisting conditions—such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, and obesity—compound cardiovascular risk. Management includes
blood sugar, lipid, and blood pressure control, often through lifestyle interventions and medications like statins, antihypertensives, and antiplatelets. Newer antidiabetic drugs like SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists have demonstrated heart-protective effects. Regular cardiovascular screening is crucial for early detection. Integrating cardiometabolic care into diabetes management can significantly reduce mortality and improve long-term outcomes.
Diabetes in adolescents presents unique challenges, including hormonal fluctuations, emotional stress, and evolving self-management skills. Both type 1 and
type 2 diabetes are increasingly prevalent in this age group. Adolescents may struggle with adherence to
insulin regimens, dietary restrictions, and lifestyle changes. Peer pressure and body image concerns can affect disease management. Multidisciplinary support involving pediatric endocrinologists, psychologists, and educators is crucial. Early intervention, family involvement, and school-based education promote better outcomes. Technology like insulin pumps and CGMs aids in control. Empowering adolescents to understand and manage their condition fosters independence and reduces future complications.
Diabetes during pregnancy, including preexisting
diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), poses risks to both mother and baby. It increases the chances of preeclampsia, preterm birth, macrosomia, and neonatal hypoglycemia. Tight glycemic control before and during pregnancy is essential to reduce complications. Management involves frequent glucose monitoring, tailored nutrition, insulin therapy, and regular fetal assessments. Women with GDM have a higher risk of developing
type 2 diabetes later in life. Postpartum screening and lifestyle counseling are vital. Collaborative care between obstetricians, endocrinologists, and dietitians ensures safe outcomes and promotes long-term health for both mother and child.
Market Analysis
The global diabetes market is witnessing robust growth due to the rising prevalence of the disease, advancements in technology, and increased healthcare spending. As of 2024, over 537 million adults are living with diabetes, and this number is projected to reach 643 million by 2030, according to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF). This surge has fueled demand for diagnostic tools, insulin delivery devices, medications, and digital health platforms. The global diabetes care market was valued at USD 65 billion in 2023, and it is expected to surpass USD 90 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.8%. North America remains the dominant market due to high awareness, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and strong insurance systems. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by increasing urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, and rising obesity rates.
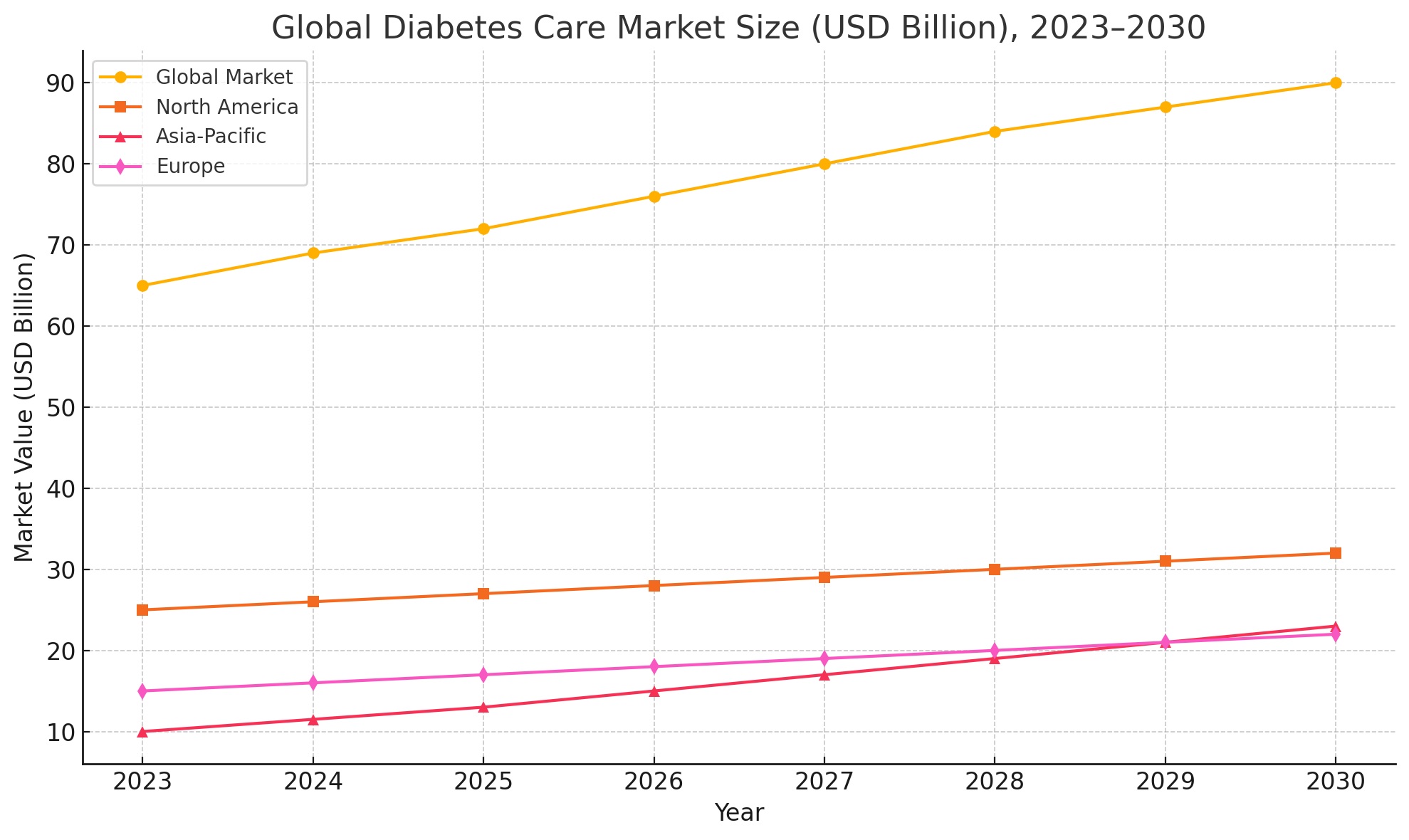
Technological advancements, especially in Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM), Artificial Pancreas systems, and AI-driven analytics, are transforming diabetes care and management. Pharmaceutical giants such as Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, and Medtronic are investing heavily in R&D to develop innovative treatments and digital solutions. Governments and health agencies are increasingly focused on preventive care and early diagnosis, with mobile health (mHealth) and telemedicine platforms gaining traction. Furthermore, the demand for personalized and precision medicine is expected to redefine future treatment protocols.
In conclusion, the diabetes market presents significant opportunities for innovation, investment, and collaborative healthcare models. A multidisciplinary approach combining medicine, technology, and lifestyle management is essential to curb the global diabetes burden.
Why to attend
37th International Congress on Prevention of Diabetes and Complications gives you an opportunity to broaden your thinking and knowledge by listening to ideas and theories and recent developments in diabetes care. Diabetes Meeting 2026 conference can give you a wonderful opportunity to meet and interact with fellow researchers, experts across the World. It also allows you to meet new people.
Benefits of attending:
1. Learn from Top Professionals all over the world.
2. be familiar with the latest trends and challenges within your sector.
3. Share your research with top professors and get instant answers to your queries.
4. Participate in panel discussion session including live Q&A
This Diabetes Meeting 2026, will be a truly international event; we expect to welcome healthcare professionals from over 100 countries. We also have global faculty who are leading experts in their fields. Gain valuable awareness from these prominent professionals from skilled institutions.
Benefits of Joining Conference:
-
Get your abstract published with DOI
-
Get Certified for your participation
-
Reduced Costs Affordability
-
Knock Down Geographical Barriers
-
Convenience from comfort of your own home or from work
-
They’re Archived: Ability to view events in the recording
-
Great resource for learning new career skills
-
Learn from the Pros
-
Global exposure to your research
-
Make new connections
-
Significant time saving
-
Increased engagement
-
Wider Reach
-
More Engaging
-
Position yourself as the expert
Salient features
-
Keynote speeches and plenary talks by researchers all over the globe
-
Opportunity to meet globe expert’s in regenerative medical science
-
Posters, e-posters and video presentation by research community
-
International Certification by Organizing Committee
-
Publishing accepted abstracting International Journals
-
The study provides an in-depth analysis of the global Cardiology market
Target Audience
-
Diabetologists
-
Endocrinologists
-
General practitioners
-
Nurses
-
Students
-
Diabetes educators
-
Pharmacists and dietitians
-
Researchers and clinical scientists
-
Healthcare professionals
-
Policymakers and stakeholders
-
Diabetes patients
CME & CPD Credits
CME Credits:
Continuing Medical Education (CME) refers to a specific form of continuing education that helps medical professionals to maintain competence and learn about new and developing areas of their field. Conference Series Conferences are recognised and accredited with CME credits to enhance the professional abilities and skills of participants. CME credits are important to physicians because they require a specified number of credits annually to maintain medical licenses. CME credits are authorized by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education. Attending CME accredited conference is beneficial and valuable to physicians and other medical professional as it is a source of constant improvement that ultimately improves their medical practice, and keeps them up-to-date on the latest technologies, advancements, treatments, etc. Speaking at CME activities can also be a great stage for clinical medical professionals to share their expertise and increase their distinction in their specialty.
CE Credits:
Continuing Education (CE) credit is a measure used in continuing education programs to assist the professional to maintain his or her license in their profession. Conference Series Conferences provides ample opportunities to acquire CE credits. CE can open up previously closed doors and lead to better job opportunities. CE usually refers to college courses or other vocational training obtained by older adults or working professionals. CE credits work as carrier promoter and hold great value in medical, clinical and other areas of research even after completion of degrees in concerned field of research. It is pivotal in today’s world to get updated information on your field of research and profession. Attending Continuing Education Conferences can help expand your network and make connections that could translate into profitable relationships or job opportunities down the line. It also plays a vital role in recruiting new team members for an employer with open positions. CE helps licensing organizations and professional membership groups. Continuing Education promotes high quality performance, keep professionals up to date with the latest advances, and provide excellent networking opportunities.
CPD Credits:
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) is the holistic commitment of professionals towards the enhancement of personal skills and proficiency throughout their careers. It enables learning to become conscious and proactive, rather than passive and reactive. CPD accreditation is important because it ensures that courses provided adhere to the highest educational standards and international benchmarks of quality and learning. CPD enriches your knowledge, keeps you currently competent and is the key to career progression and professional growth. There are many advantages to carrying out CPD that includes filling gaps in your knowledge and skills to become more productive and efficient, building confidence and credibility to stand out from the crowd, achieving your career goals and demonstrating professional status. CPD hours can be earned through continuing education, leadership activities, instructional activities, completion of significant work projects, research and publications. Conference Series Conferences have been accredited with CPD credits to expedite the progress of research and industry professionals.
Past Conference Report
36th International Congress on Prevention of Diabetes and Complications was organized during April 07-08, 2025, at Pacific Gateway Hotel, 3500 Cessna Dr, Richmond, BC V7B 1C7, Canada. The conference was marked with the attendance of Editorial Board Members of supporting journals, Scientists, young and brilliant researchers, business delegates and talented student communities, who made this conference fruitful and productive, This conference was based on the theme “
New technologies, devices, and treatments in diabetes care” which included the following scientific tracks:
We taken the privilege of felicitating
37th International Congress on Prevention of Diabetes and Complications which will be held during April 27-28, 2026 in Rome, Italy. We cordially welcome all the Organizing Committee, Editorial Board Members and Keynote Speakers who supported for the success of this conference, The esteemed guests, keynote speakers and researchers shared their innovative research and vast experience through their informative presentations at the podium of
Diabetes Meeting 2026. We are glad to inform that all accepted abstracts for the conference have been published in our respective journals.






















